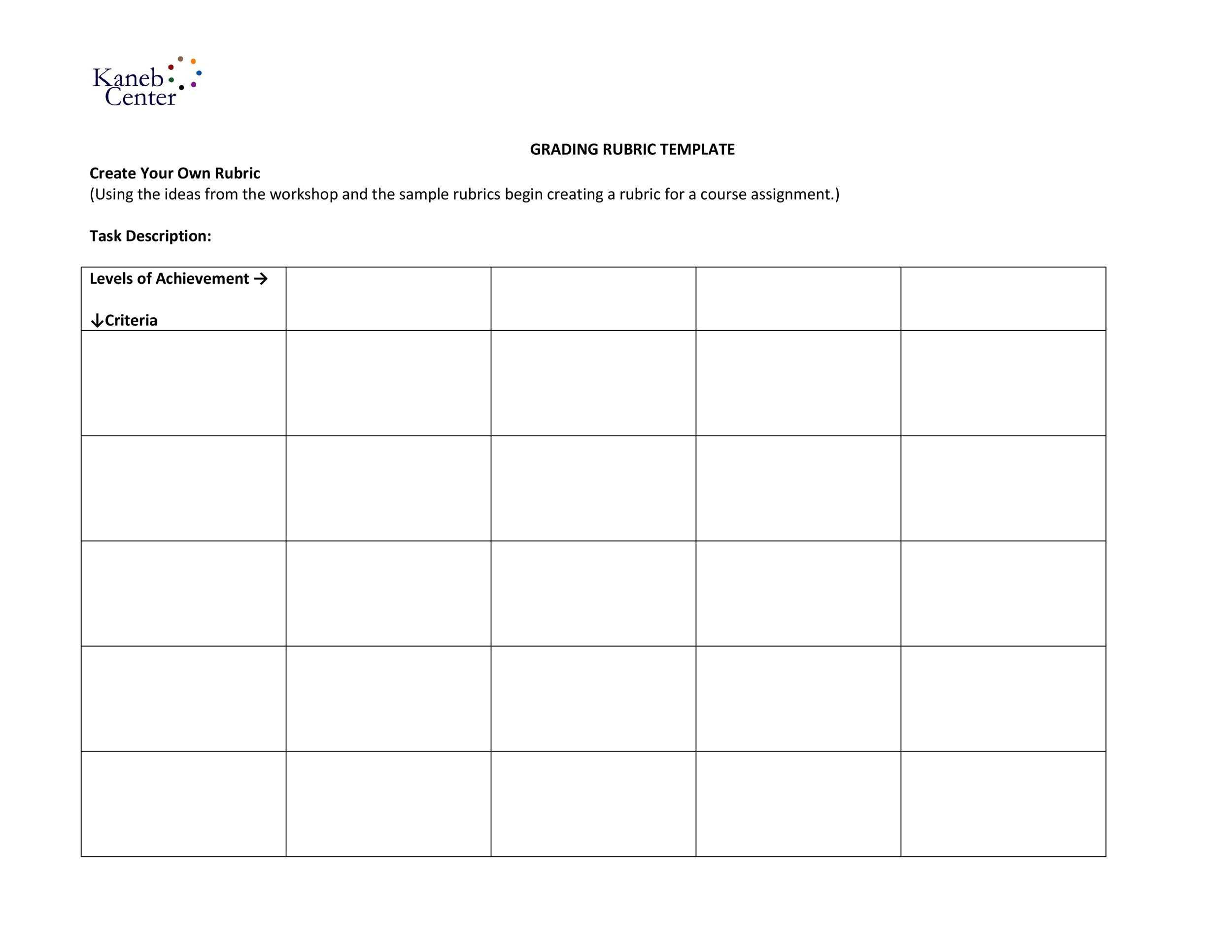
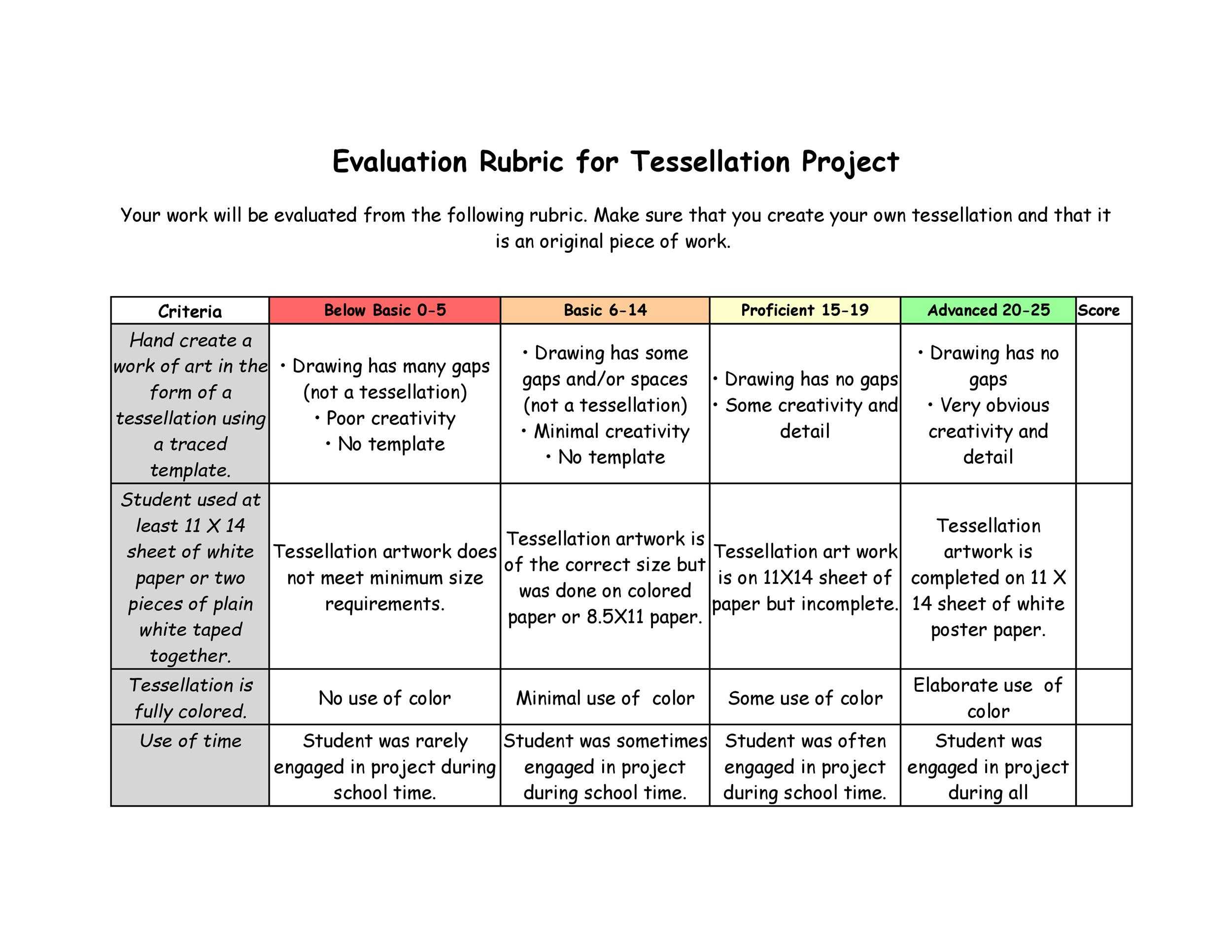
A rubric, or “a cast that provides levels of accomplishment for a set of criteria” (Howell, 2014), is a accepted apparatus for assessing open-response or artistic appointment (writing, presentations, performances, etc.). To use rubrics effectively, advisers should accept their benefits, the types and uses of rubrics, and their limitations.
The belief articular in the cast differs with the accountable matter, the attributes of the assignment, and acquirements objectives, but all rubrics serve three purposes.
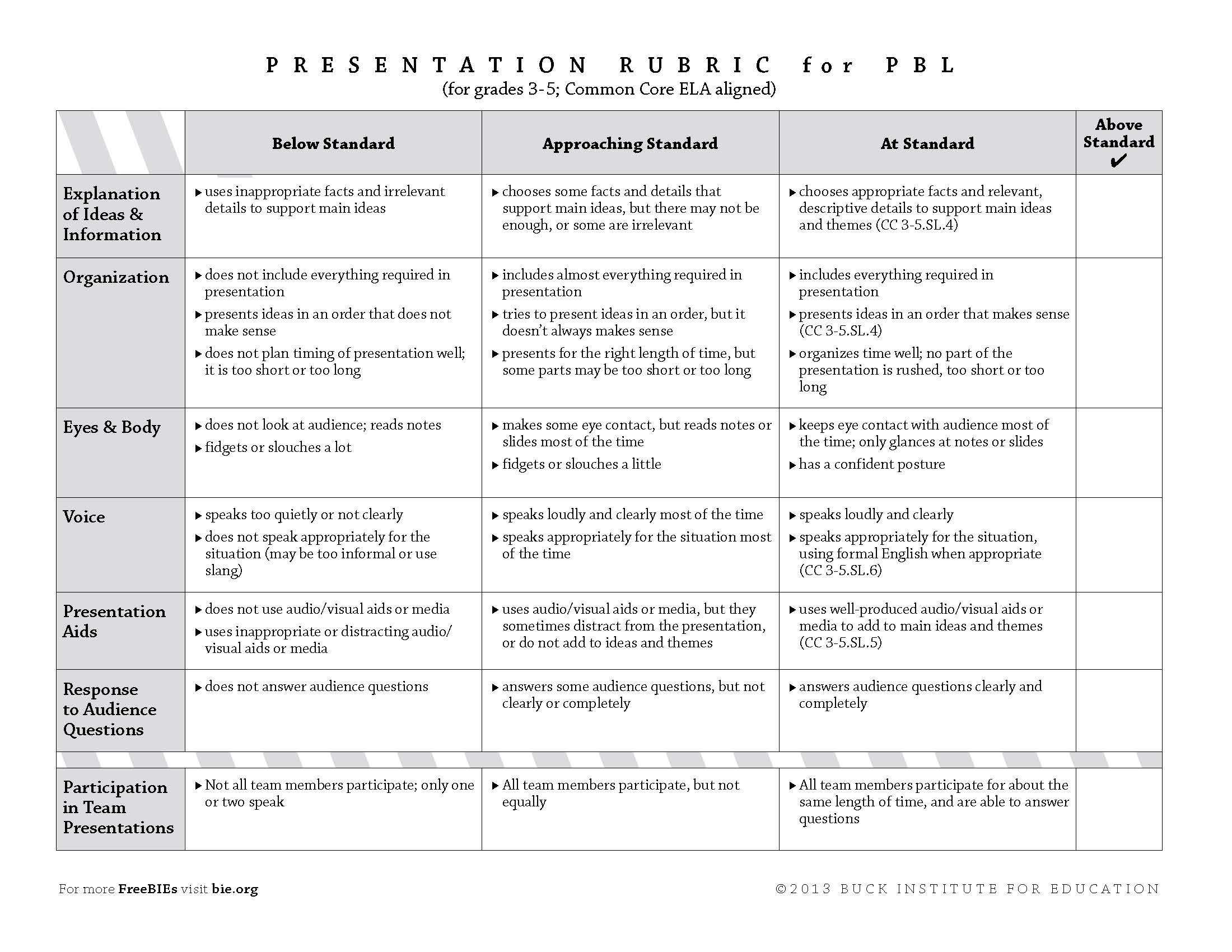
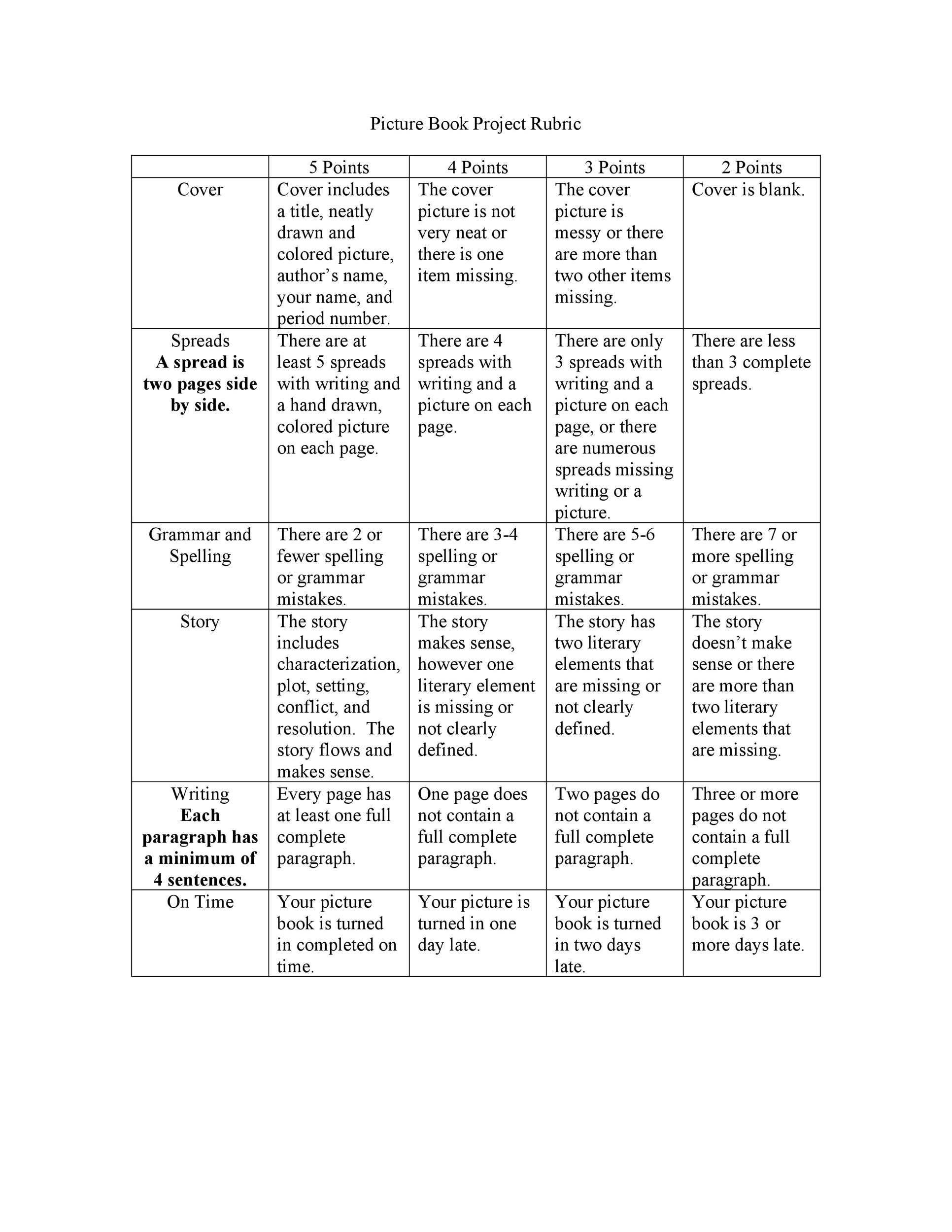
There are two basal types of rubrics. Holistic rubrics accommodate an all-embracing description of appointment at assorted levels of achievement. For instance, abstracted paragraphs ability call “A,” “B”, “C,” and “D” -level papers. A holistic explanation ability advice advisers acquaint the interrelationships of the elements of an assignment. For instance, acceptance should accept that a absolutely actuating analysis cardboard not alone has able altercation and affirmation but is additionally chargeless of autograph errors. These rubrics action anatomy but additionally allow adaptability and acumen in grading.
A-Level
This branch describes what an A-level acquiescence looks like overall.
B-Level
This branch describes what a B-level acquiescence looks like overall.
C-Level
This branch describes what a C-level acquiescence looks like overall.
D-Level
This branch describes what a D-level acquiescence looks like overall.
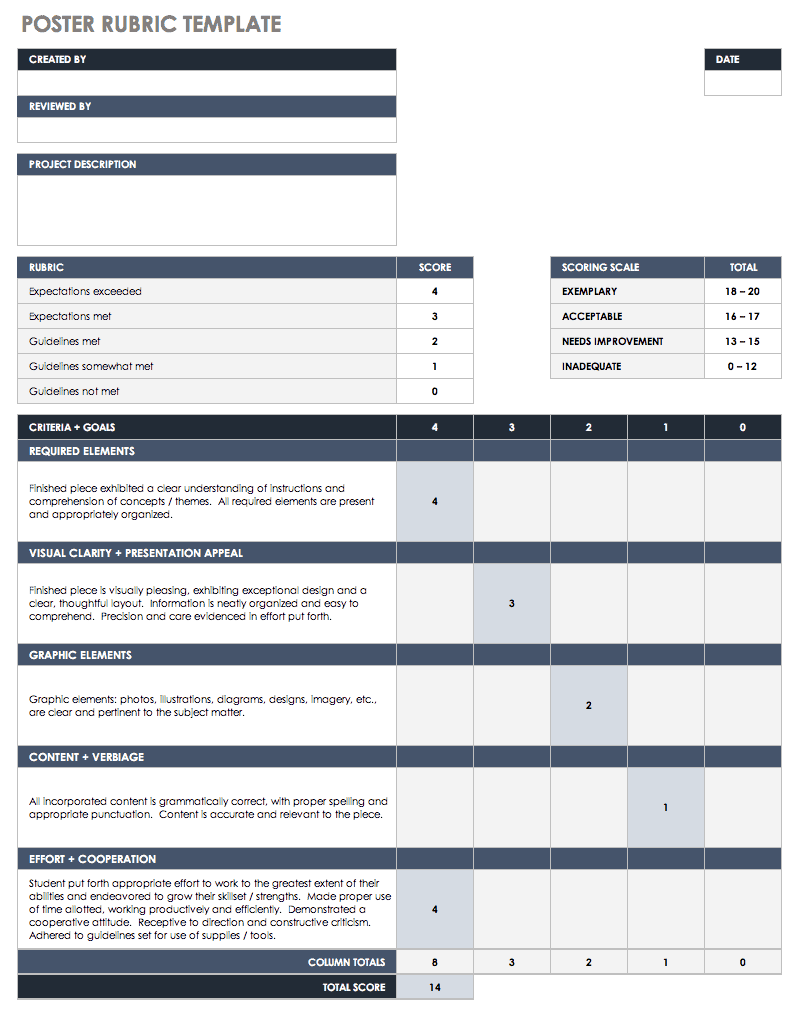
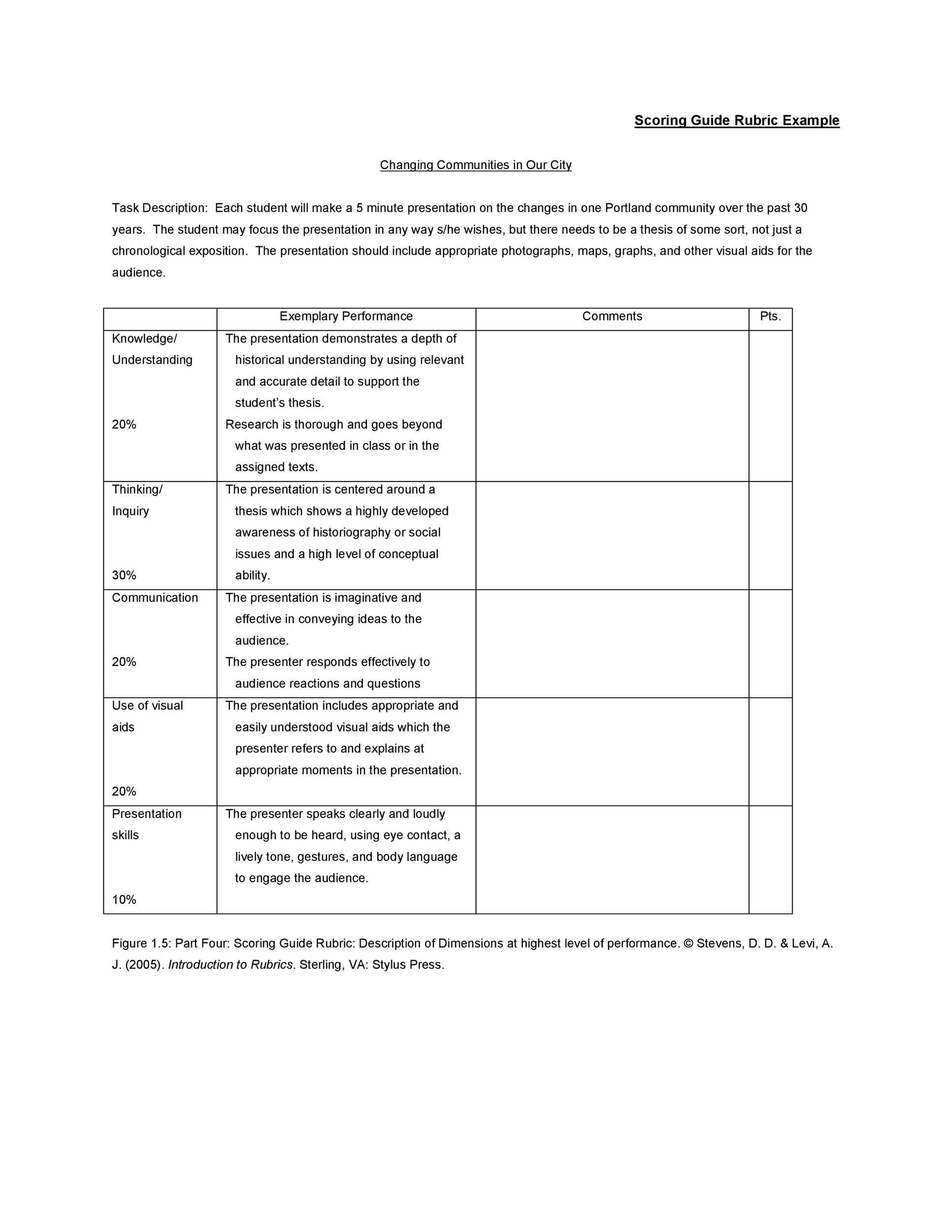
Analytic rubrics accommodate added abundant descriptions of accomplishment levels of audible apparatus of the assignment. For instance, the apparatus of thesis, evidence, coherence, and autograph mechanics ability anniversary be declared with two to three sentences at anniversary of the accomplishment levels. Such rubrics advice advisers and acceptance abstract detached abilities and performance. These rubrics absolute the grader’s acumen and potentially action greater consistency.
Component 1
(x points)
Component 2
(x points)
Component 3

(x points)
Component 4
(x points)
Whether designing a holistic or analytic rubric, the descriptions of apprentice accomplishment levels should absorb accepted apprentice mistakes. This saves time as it reduces the charge for long-hand acknowledgment that is time-consuming and generally adamantine for acceptance to apprehend (Stevens and Levi, 2013). For either blazon of rubric, the accomplishment akin may be adumbrated with evaluative autograph (e.g., Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor) or brand labels (A, B, C, D). In abounding cases, rubrics additionally accommodate the point totals accessible with all-embracing akin (holistic) or anniversary basic (analytic).
Developing a explanation requires anecdotic and belief the altered elements of an assignment. The about weight accustomed to any class should reflect the acquirements objectives. For instance, if the acquirements objectives focus on interpreting and application evidence, the weight of the brand should not abatement on abecedarian skills, like grammar and syntax. At the aforementioned time, rubrics can advice advisers bright and apparatus adorning goals. For example, application the aforementioned elements for two or added iterations of an assignment, the explanation for an beforehand acquiescence can abode added weight on autograph mechanics, while added weight can be placed on higher-order abilities for a after submission.
Rubrics can be acclimated as accumulative or determinative assessment. Acclimated as accumulative assessment, rubrics accord accurate account for the brand that acceptance receive. Acclimated as determinative assessment, rubrics advice both advisers and acceptance adviser the areas in which acceptance are afterwards and struggling. For best use of rubrics as determinative assessment, allocation should be accompanied by clear, improvement-oriented acknowledgment (Wylie et al., 2013). Additionally, advisers can crave acceptance to use the explanation as a account that they about-face in with their work. This may advice acceptance bigger adviser the affection of their appointment afore appointment it (Treme, 2017).
Technology can aid in developing and application rubrics. Canvas provides a explanation architect action that gives options for allotment point value, abacus comments, and anecdotic belief for the assignment. To admission it, go to the “assignments” page, bang on the assignment, and baddest “add rubric.” A technologically-developed explanation like those in Canvas ensures greater bendability in allotment grades (Moyer, 2015).
No explanation is a complete acting for articular judgment. While advisers strive to abolish arbitrariness in grading, able accurateness is consistently an additive in assessment. Despite their air of objectivity, rubrics absorb cogent subjectivity—for instance, in the decisions about the about weight or the descriptions of elements of apprentice work. Nor are rubrics a “silver bullet” for accomplishing aerial bookish performance. Baseline ability and above-mentioned bookish accomplishment are still greater factors in apprentice accomplishment (Howell, 2014: 406). Nonetheless, rubrics are a advantageous apparatus for announcement consistency, transparency, and objectivity and can accept absolute outcomes for advisers and students.

Howell, R. J. (2014). Allocation rubrics: Hoopla or help? Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 51(4): 400-410.
Kryder, L. G. (2003). Allocation for speed, consistency, and accuracy. Business Communications Quarterly, 66(1): 90-93.
Moyer, Adam C., William A. Young II, Gary R. Weckman, Red C. Martin, and Ken W. Cutright. “Rubrics on the Fly: Improving Efficiency and Bendability with a Rapid Allocation and Acknowledgment System.” Journal of Teaching and Acquirements with Technology, 4, no. 2 (2015): 6-29.
Stevens, D., & Levi, A. (2013). Introduction to rubrics: an appraisal apparatus to save allocation time, back able feedback, and advance apprentice acquirements (Second edition.). Sterling, Virginia: Stylus.
Treme, Julianne. “An Op-Ed Allocation Rubric: Improving Apprentice Output and Professor Happiness.” NACTA Journal, 61, no. 2 (2017): 181-183.
White, Krista Alaine, and Ella Thomas Heitzler. “Effects of Increased Evaluation Objectivity on Brand Inflation: Precise Allocation Rubrics and Rigorously Developed Tests.” Nurse Educator, 43, no. 2 (2018): 73-77.
Wylie, Caroline and Christine Lyon. “Using the Determinative Rubrics, Reflection and Observation Tools to Support Professional Reflection on Practice.” Determinative Appraisal for Teachers and Acceptance (2013).
Checklist Rubric Template – Checklist Rubric Template
| Encouraged to my personal website, in this particular time I’m going to show you in relation to Checklist Rubric Template
.
Why not consider graphic above? is actually that will awesome???. if you feel consequently, I’l d demonstrate a few graphic once more underneath:
So, if you’d like to receive all of these incredible shots about Checklist Rubric Template, click save link to download the photos to your personal pc. They are all set for save, if you appreciate and want to take it, simply click save logo in the web page, and it will be directly saved to your laptop.} At last if you would like have unique and latest image related with Checklist Rubric Template, please follow us on google plus or book mark this site, we attempt our best to give you regular up-date with all new and fresh graphics. Hope you love staying right here. For some updates and latest information about Checklist Rubric Template shots, please kindly follow us on tweets, path, Instagram and google plus, or you mark this page on book mark area, We try to give you up-date periodically with all new and fresh photos, love your browsing, and find the perfect for you.
Thanks for visiting our site, contentabove Checklist Rubric Template published . Today we’re delighted to declare we have discovered an awfullyinteresting topicto be pointed out, that is Checklist Rubric Template Some people attempting to find details aboutChecklist Rubric Template and definitely one of them is you, is not it?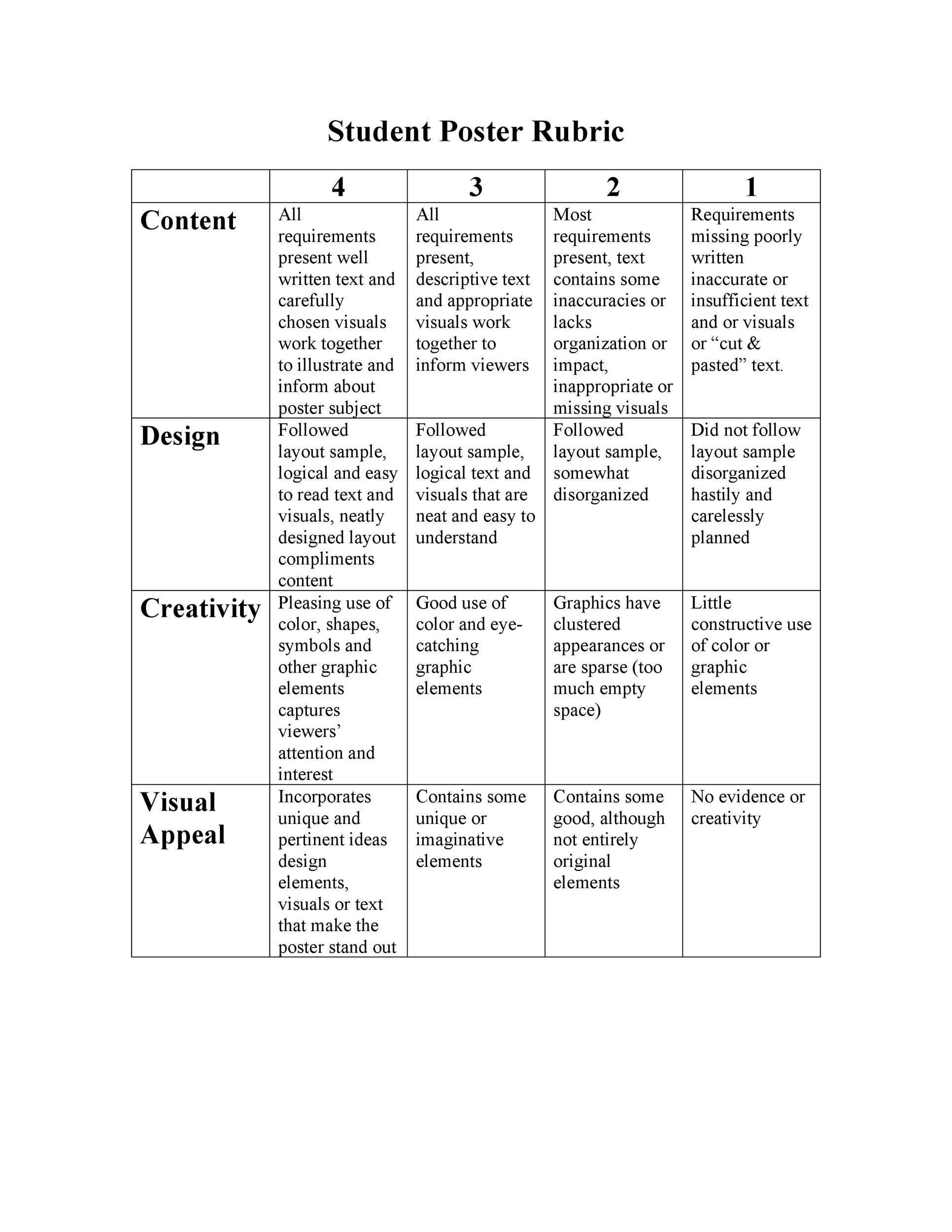
[ssba-buttons]